Matlab coder, simulink and concurrent execution
Estimated reading time: 3 minutesIn this post we show how CasADi codegen can be integrated seemlessly with Matlab Coder, Simulink and parallel execution. This requires Casadi 3.8
Some context
We discussed Matlab Coder before, in the matlab Coder blog post. There, we hinted at the application of coder.target('MATLAB') to the Matlab System of the MPC blog post.
Here, we implement that idea, and futher it to a robust thread-safe solution.
The post does go a bit deeper into the details than usually.
Starting point
We use the Matlab System block developed in the earlier blogpost:
classdef casadi_block < matlab.System
methods (Access = protected)
function num = getNumInputsImpl(~)
num = 2;
end
function num = getNumOutputsImpl(~)
num = 1;
end
...
function setupImpl(obj,~,~)
...
end
function u = stepImpl(obj,x,t)
end
function resetImpl(obj)
end
end
end
Adding coder instructions
Next, we add coder instructions for incref and decref. These have been part of the CasADi codegen API since forever, yet they were always unused up to now, and may have been missing from previous examples or tutorials.
classdef fcn_system < matlab.System
properties (Access = private, Nontunable)
name
src_name
end
methods (Access = protected)
function num = getNumInputsImpl(obj)
obj.name = 'foo';
obj.src_name = 'bar';
if coder.target('MATLAB')
% Codegen via a CasADi Function
F = opti.to_function(obj.name,{p},{x});
% Generate C code
F.generate([obj.src_name '.c'],struct('unroll_args',true,'with_header',true));
% Generate meta-data
config = struct;
config.sz_arg = F.sz_arg();
save([obj.src_name '_config.mat'],'-struct','config');
end
num = 1;
end
function num = getNumOutputsImpl(~)
num = 1;
end
function setupImpl(obj,~,~)
if coder.target('MATLAB')
else
coder.ceval([obj.name '_incref']);
end
end
function releaseImpl(obj)
if coder.target('MATLAB')
else
coder.ceval([obj.name '_decref']);
end
end
end
end
We chose to piggyback our symbolic CasADi code and code-generation into getNumInputsImpl because that routine always gets evaluated in matlab interpreted context. This stands in contrast with setupImpl which may or may not get executed in an interpreted context depending on the Simulink settings.
We will eventually have multiple Simulink blocks running in parallel. Simulink makes sure that the setupImpl and releaseImpl happen in serial mode, which is required for incref/decref. This level of granularity seems to be beyond the capabilites of a Matlab function block, so that’s why we work with a Matlab System block.
A single-threaded system
We now have a Simulink model with two instances of the System. This could be a simple model for a cascaded/hierarchical MPC.
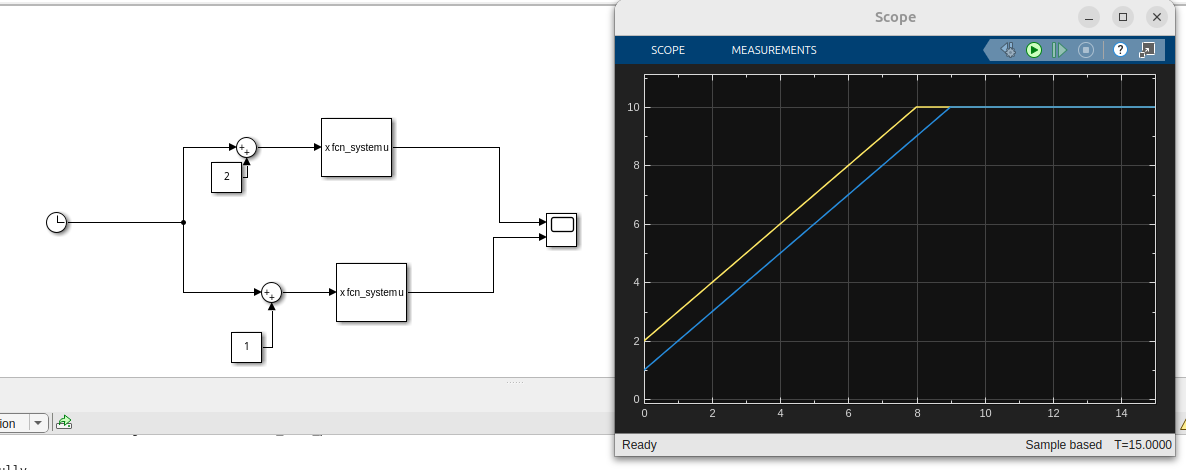
Single threaded evaluation
This will run fine with Normal, Accelerator or Rapid Accelerator modes.
Thread-safe checkout/release in codegen
This improvement can be found in the changelist.
This requires some changes in the code-gen:
F.generate([obj.src_name '.c'],struct('unroll_args',true,'with_header',true,'thread_safe',true));
And in the coder instructions:
coder.updateBuildInfo('addDefines','CASADI_MAX_NUM_THREADS=2');
coder.updateBuildInfo('addDefines','CASADI_THREAD_TYPE=CASADI_THREAD_TYPE_POSIX');
Note that we have only tested this with POSIX at the moment.
Multi-threading within a Simulink system
This section has nothing to do with CasADi really, but only with the “concurrent execution”
We follow the official cookbook to map each block to a separate thread.
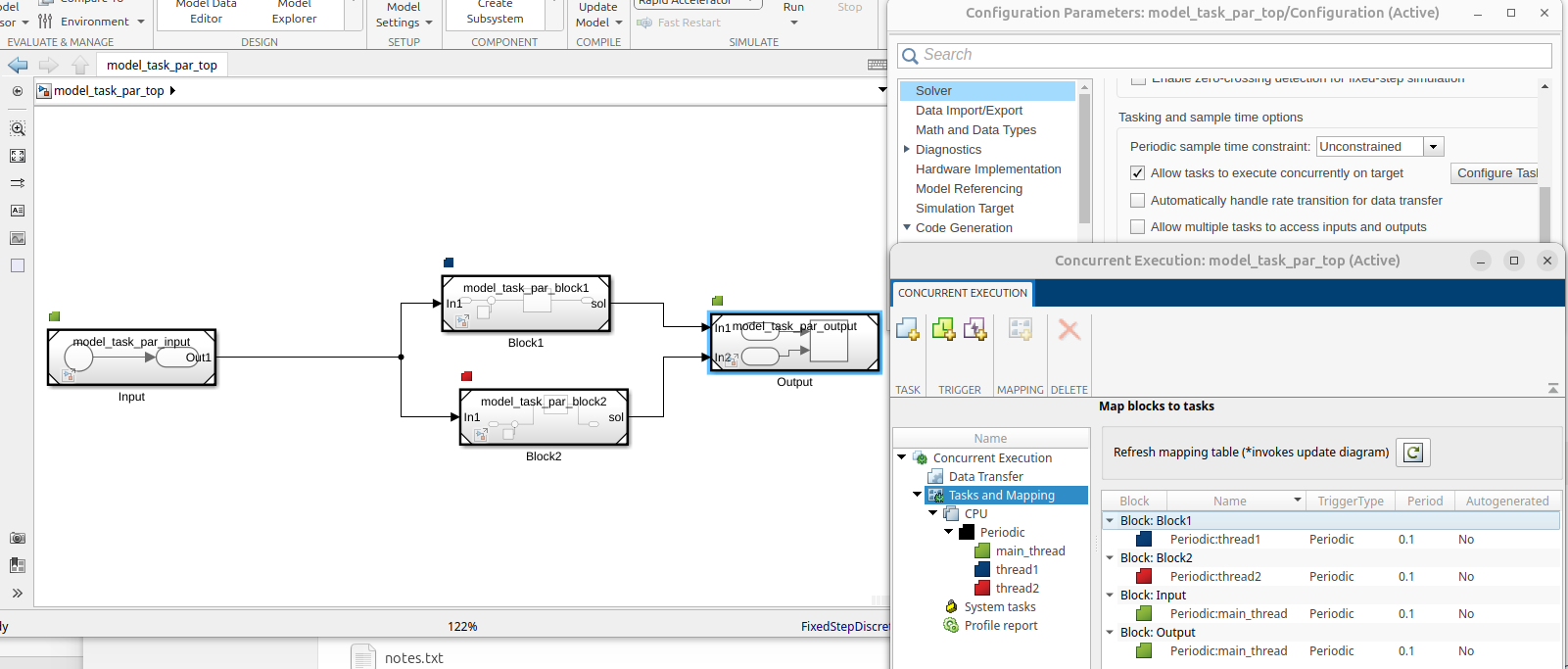
Multi threaded evaluation
Basically, we have one master Simulink model, model_task_par_top and then several sub-models each in their own slx file.
Validation
We use the following command to invoke Matlab coder, Simulink compilation and monitored running.
Simulink.architecture.profile('model_task_par_top');
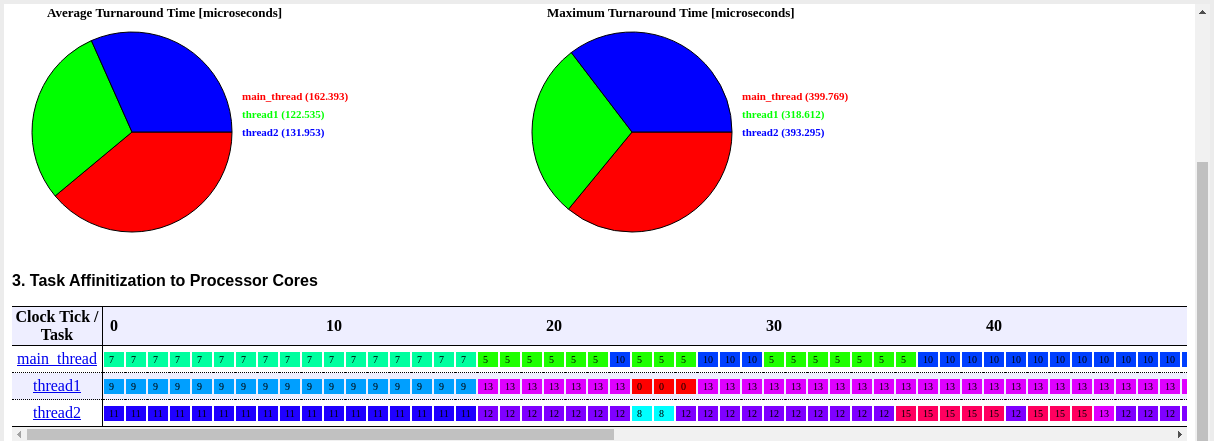
Profiling report
The code generated by Matlab Coder should look familiar to advanced CasADi users:
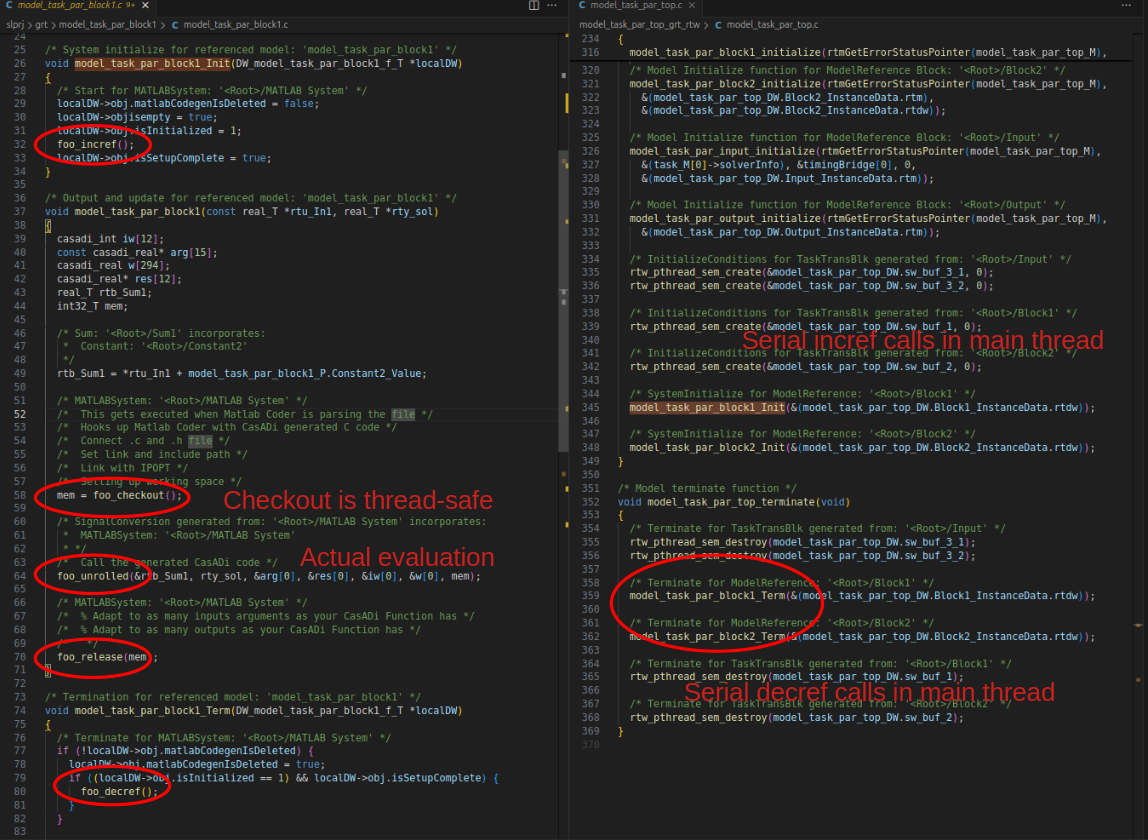
Code generated by Matlab Coder
Results
We gave a tour of advanced integration of Simulink with CasADi code-generation in a context of multi-threading.
Downloads: model_task.slx, fcn_system.m, model_task_par_top.slx, model_task_par_block1.slx, model_task_par_block2.slx, model_task_par_input.slx, model_task_par_output.slx